PROJECT LIST
| No. | Project Title | Period | Funding |
|---|---|---|---|
| C4. | Data Analysis Framework for Energy Benchmarking of Existing Buildings | 2023-2026 | Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement (KAIA) |
| C3. | Plus Energy Building Innovative Technology Research | 2020-2027 | National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) |
| C2. | 3D Urban Microclimate Prediction System | 2020-2025 | National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) |
| C1. | Hydrogen-based Energy Network Design and Operation | 2020-2024 | Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement (KAIA) |
| P5. | A Living-lab-based Occupant-responsive Housing Welfare Service for The Elderly | 2019-2022 | National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) |
| P4. | B-bem. The Bayesian Building Energy Management | 2014-2017 | Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) |
| P3. | Proactive Energy Management for High-performance Buildings | 2012-2013 | United States Department of Energy (DOE) |
| P2. | Chicago Loop Retrofit | 2011-2013 | United States Department of Energy (DOE) |
| P1. | Bayesian Calibration and Uncertainty Quantification | 2011-2013 | United States Department of Energy (DOE) |
PROJECT DETAIL
This project is a 4-year project (2023-2026), funded by Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement.
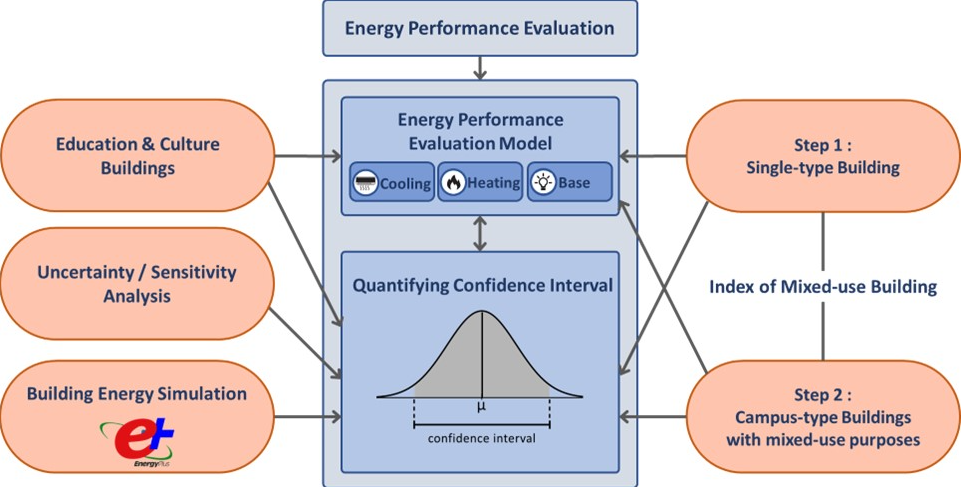
The objective of our research is to develop the analysis framework for energy benchmarking of existing buildings on the basis of public data alone. We have been developing the building benchmarking methodology that improves the reliability of benchmarking results when only public data are used. In addition, we have been developing the uncertainty quantification methodology that incorporates uncertainty due to lack of detailed data in building energy benchmarking.
This project is a 7-year project (2020-2027), funded as one of Engineering Research Centers by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
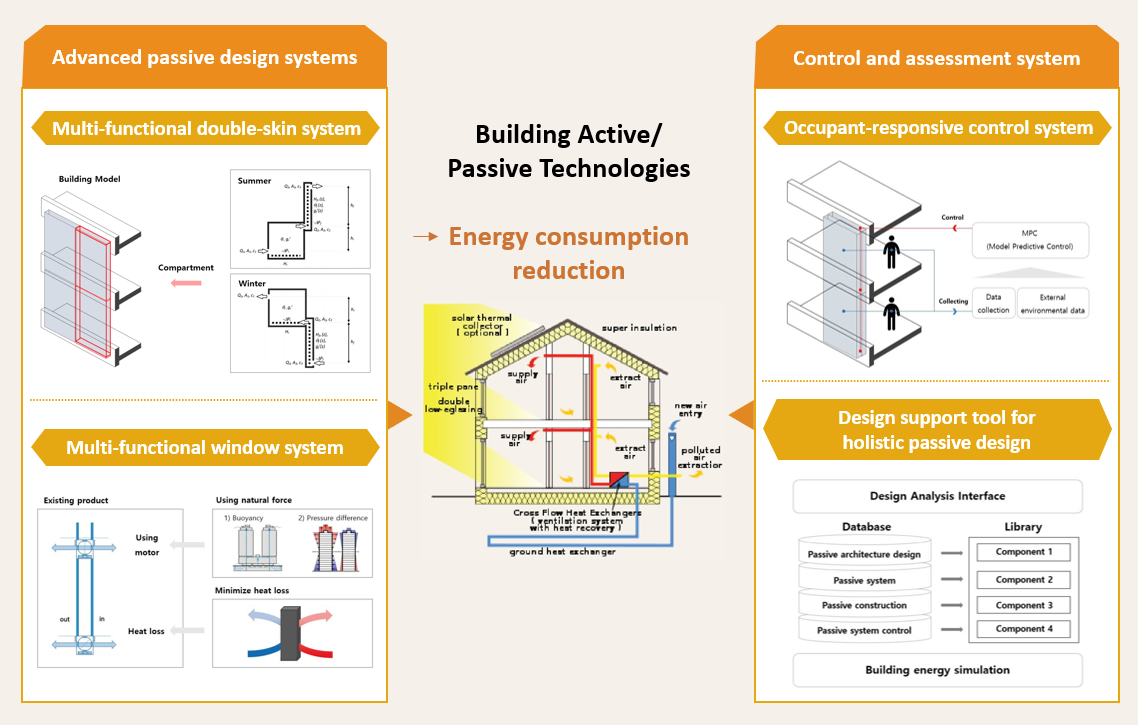
This project aims to develop advanced technologies for passive design, energy generation, and storage systems integrated to buildings. This project is being carried out in collaboration with the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Korea University), Korea Institute of Energy Research, and Korea Institute of Construction Technology. In this project, our role is to develop advanced passive design systems, particularly double-skin facade and total window systems that exploit the potentials of passive heating, cooling and natural ventilation. In the later stage, occupant-responsive control algorithms will be developed to optimize the performance of passive design systems under dynamic weather conditions and stochastic occupant behavior. In addition, a comprehensive assessment system will be delivered as a tool to support design of plus energy buildings in practice.
The 3D urban microclimate prediction system is being developed in a 5-year project (2020~2025), funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
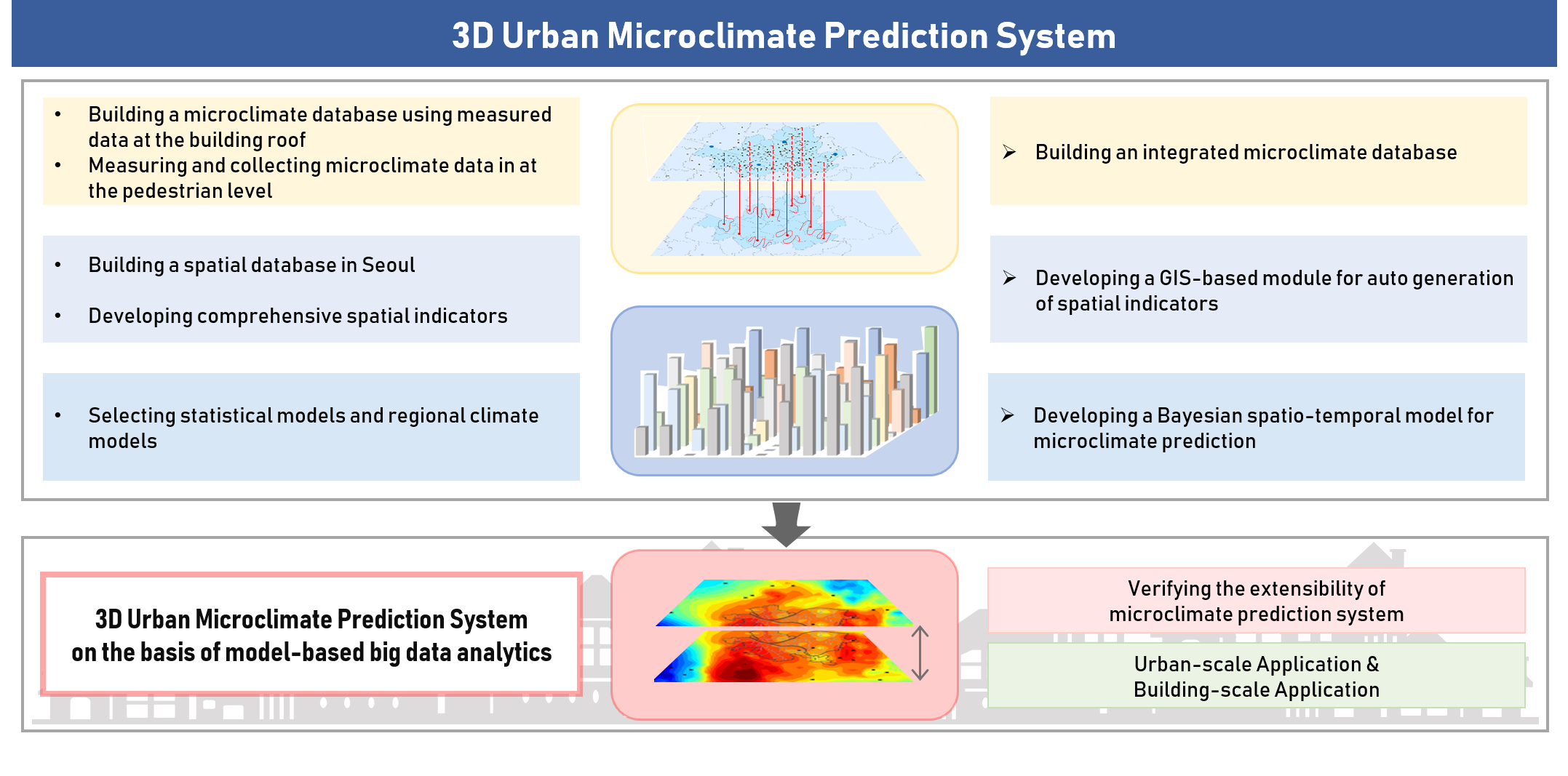
The aim of this project is to develop the 3D urban microclimate prediction system on the basis of model-based big data analytics. Beyond the existing urban climate models on the basis of urban average density measures, the project will develop a new microclimate prediction model that allows for predicting the thermal environment in the city by location and height with a full consideration of complex urban morphology. The project will develop a Bayesian spatio-temporal model that can fully exploit both urban microclimate data and existing urban climate models. The resulting microclimate prediction system will be applied to establish effective microclimate mitigation plans at urban/building scales.
This project is being developed in a 4-year project (2020-2024), funded by the KAIA (Korea Agency for Infrastructure Technology Advancement).
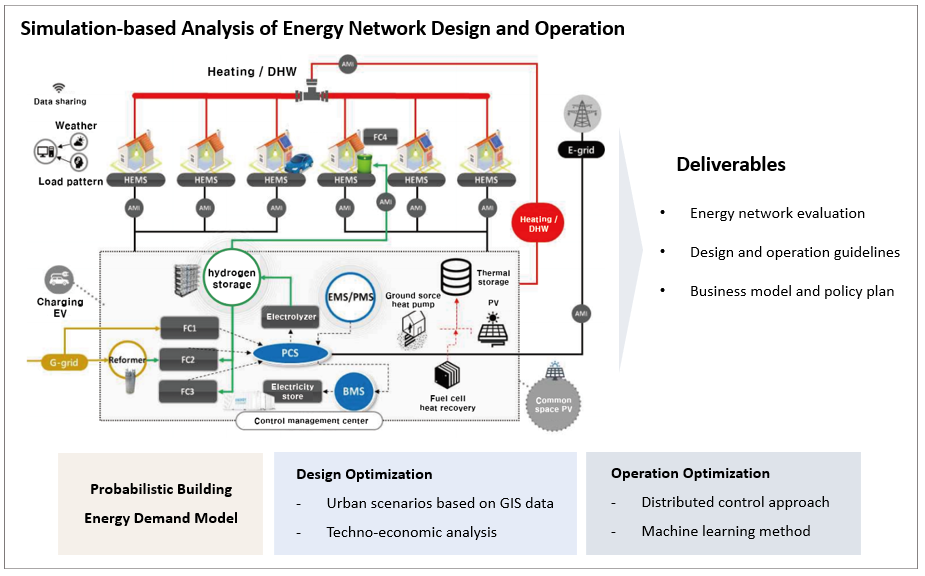
This project aims to advance and demonstrate renewable energy supply systems based on hydrogen and prosumer buildings for local energy communities. The project is being carried out in collaboration with Korea Institute of Energy Research, LH Institute, KEPCO E&C, and Korea Institute of Construction Technology. In this project, we are developing guidelines to optimize design and operation of hydrogen-based energy networks for various types and scales of communities. In addition, we will develop new business models and necessary policies to accelerate adoption of hydrogen-based energy networks in local communities.
A Living-lab-based Occupant-responsive housing welfare service for the Elderly is being developed in a 3-year project (2019~2022), funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
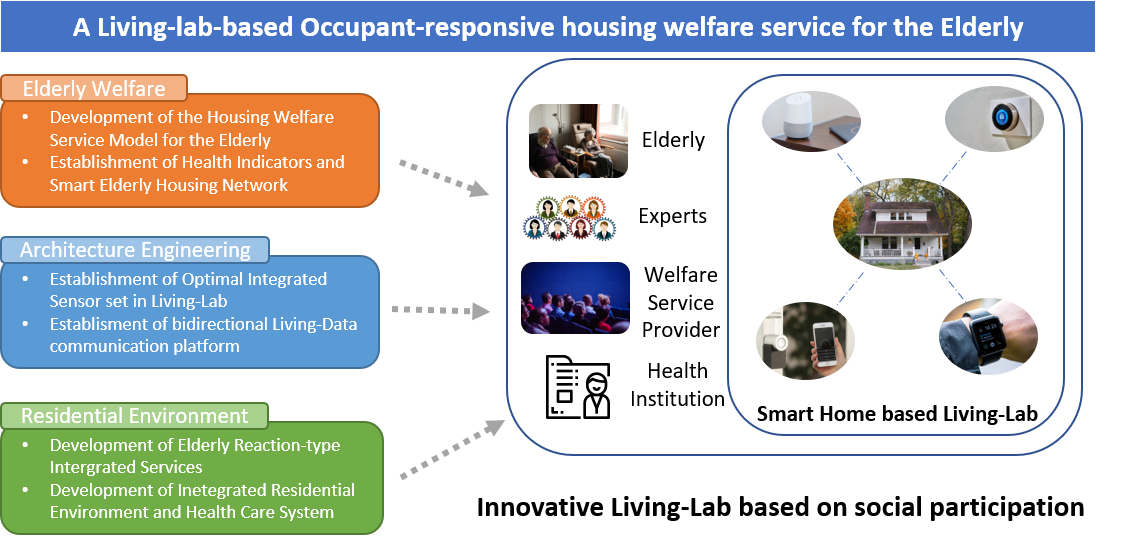
To develop occupant-responsive housing welfare service especially for the elderly, we formed the multidisciplinary research group that consists of researchers in the field of elderly welfare, architectural engineering, and interior design. We are using a variety of research methods to deliver a new welfare system based on IoT(Internet of Things), particularly for the elderly. Using Living Lab methodology as a social innovation model, social welfare researchers are defining welfare needs for the elderly and developing a home-based welfare model. In parallel, engineering researchers are developing algorithms and systems on the basis of IoT sensors and devices and testing them through an IoT-based living lab. Our ambition is to extend the functionality of smart home technologies to offer extensive welfare services for the elderly, including optimal control of indoor environments and management of health conditions and dashboard interface tailored to make various welfare services easily accessible to the elderly. We aim to deliver a new system that addresses current housing welfare problems for the elderly through Living Lab formed by service providers, researchers, and the elderly.
B.bem is being developed in a 3 year project, funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
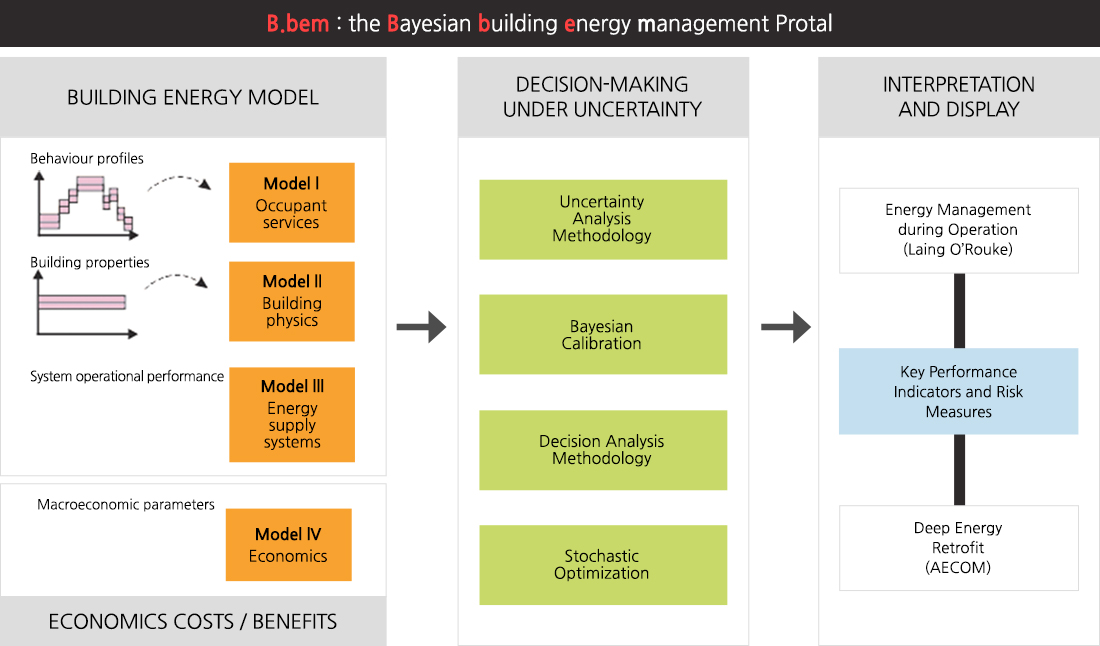
The ambition of the B.bem project is to transform conventional energy analysis processes to support the future energy management of existing non-domestic buildings - whether to assist in small-scale changes to building operations or deep energy retrofits. The aim is to quantify stochastic and operational uncertainties influencing building energy use, and to propagate those uncertainties through simulation models. B.bem, the Bayesian building energy management portal, uses computer simulation of building energy consumption to help energy managers understand the risk associated with energy management decisions.
This project was R&D project with the BuildingIQ company specialized in energy management systems and funded by the U.S. Department of Energy.
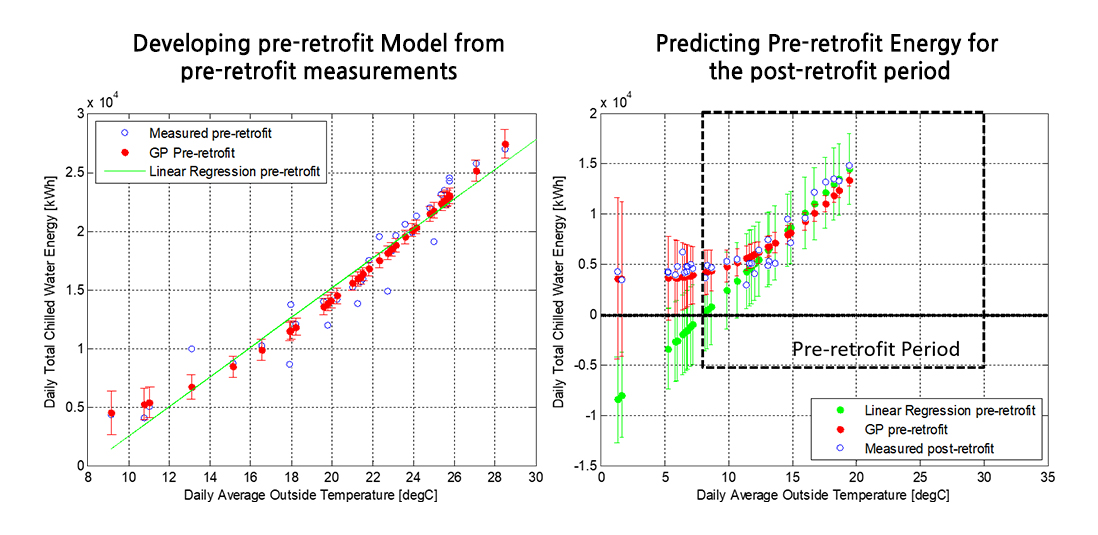
This project developed a Gaussian process (GP) modeling framework that can reliably determine energy savings and uncertainty levels for measurement and verification practices. Existing measurement and verification guidelines provide savings calculation procedures based on linear regression techniques that are limited in their predictive and uncertainty estimation capabilities. Unlike linear regression models, GP models can capture nonlinear energy behavior, multivariable interactions, and time correlations while quantifying uncertainty associated with predictions. Furthermore, the project has demonstrated the applicability of this modeling method for a model predictive control system integrated into existing energy management systems for optimizing HVAC set points.
This research project was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy.
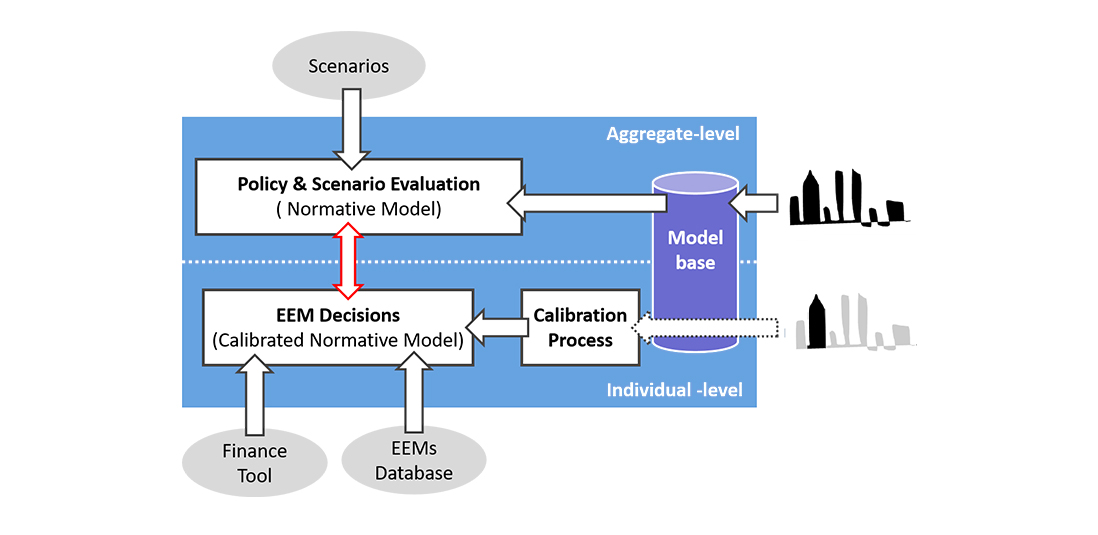
This project developed a scalable analysis methodology that supports retrofit decision-making at the individual and aggregate levels. The methodology is based on a light-weight quasi-steady-state model and Bayesian calibration. The methodology allows decision makers to evaluate policy and planning options in the context of the actual building portfolio and informs individual building stakeholders of specific retrofit strategies suited to their buildings by assessing performance risk associated with retrofit technologies. s to provide objective and transparent benchmarking and assessment. The methodology was applied to a set of commercial buildings in the Chicago Loop to support Chicago Climate Action Plan by reducing energy consumption from the building sector through energy retrofit.
This research project was funded by the Department of Energy, U.S.
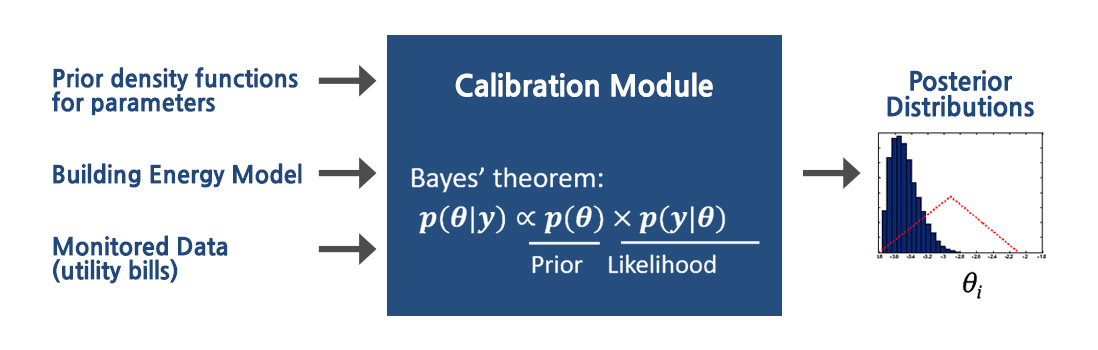
This project developed a new calibration method based on a Bayesian approach that can update model parameter values in a simulation model while quantifying uncertainty in the model. The Bayesian approach enables probabilistic outputs from the energy model, which are used to quantify risks associated with investing in energy efficiency measures in existing buildings. This research project demonstrated the efficacy of Bayesian calibration under different levels of uncertainty in the simulation model and delivered an automated process for probabilistic model calibration for implementation in an energy modeling and simulation platform (OpenStudio).